Trevor Maxwell

Translating Data To Insightful Stories
View My LinkedIn Profile
The advancement of AI piqued my interest. What started as an exploration of the emerging technology
turned into a career transition. I am excited to be working as a technical business analyst. I am
looking forward to what I will continue to learn and discover.
About the data
-
% Iron Feed: Percentage of iron being fed into the flotation cells. It refers to the iron content in the initial or incoming material.
-
% Silica Feed: Percentage of silica (silicon dioxide) being fed into floatation cells with iron. Silica is a common impurity in many ores and minerals.
-
Starch Flow: Flow rate of starch, It’s a reagent used in the flotation processes measured in m3/h (cubic meter per hour).
-
Amina Flow: Flow rate of amina, an organic reagent used as a collector in flotation processes to enhance the hydrophobicity of mineral particles measured in m3/h.
-
Ore Pulp Flow: Fow rate of the ore pulp or slurry, which is a mixture of water and finely ground ore.
-
Ore Pulp pH: The pH (acidity or alkalinity) of the ore pulp. pH control is important in flotation processes as it affects the chemical reactions and the behavior of minerals, the value must be between 0 to 14.
-
Ore Pulp Density: Concentration of the ore pulp, which refers to the mass of the ore solids per unit volume of the pulp measured in 3 kg/cm3.
-
Flotation Column XX Air Flow: Air flow rates in different flotation cells. Air flow is essential in creating the froth and carrying the hydrophobic mineral particles to the surface during flotation. Measured in Nm3/h
-
Flotation Column XX Level: The froth in different flotation cells. Monitoring the cell levels helps in controlling the flotation process. Measured in mm
-
% Iron Concentrate: Percentage of iron in the final concentrate obtained from the flotation process. It indicates the iron content in the purified or enriched product.
-
% Silica Concentrate: Percentage of silica in the final concentrate obtained from the flotation process. Measured 0-100% of how much iron is left over.
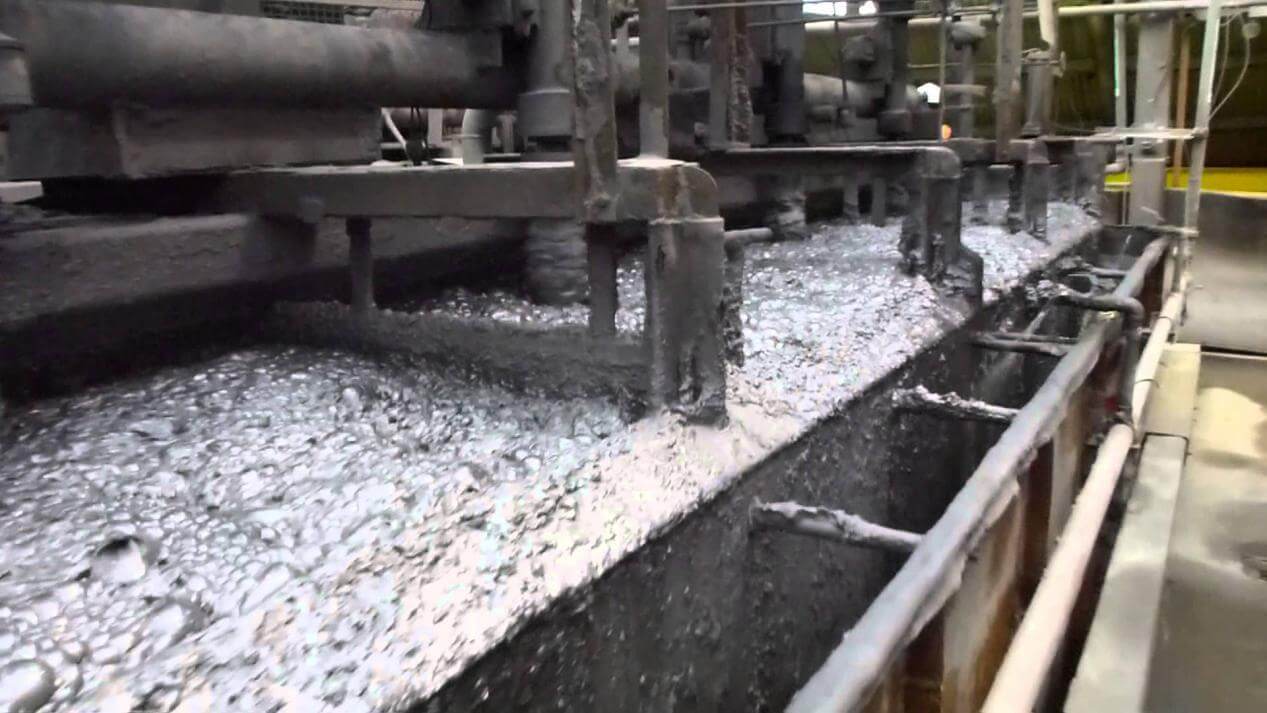

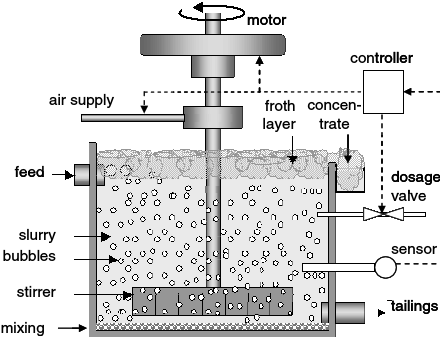
Flotation extraction is a popular method for removing precious minerals from their ore. It is very useful for extracting minerals including copper, lead, zinc, nickel, gold, and silver. The technique is based on mineral physical and chemical features, such as hydrophobicity (tendency to reject water) and density differences.
The ore is coarsely crushed and combined with water to form a slurry in a standard floating extraction process. The slurry is next treated with collectors, which are chemical reagents that improve the hydrophobic characteristics of the target material. These collectors selectively attach to the surface of the desired mineral particles, resulting in the formation of a froth on top of the slurry.
When air is added to the slurry, bubbles form that cling to the hydrophobic mineral particles in the froth. The mineral-laden froth rises to the surface, while the undesired minerals remain in the slurry. This precious mineral concentrate-containing froth is then skimmed off and further processed to yield a refined product.
To optimize the flotation process, several variables such as pH, temperature, agitation, and reagent dosage are carefully controlled. These parameters can be changed depending on the mineral properties and desired extraction efficiency.
